In a world more connected than ever, it is ironic that feelings of loneliness are increasing at an alarming rate. As we step into 2024, recent data highlights the growing concerns about the loneliness epidemic — a term used to describe the significant and rising number of people experiencing loneliness and social isolation worldwide. While technological advancements have brought the world closer digitally, the human experience of connection seems to be waning. This blog delves into the loneliness epidemic statistics across continents and explores the growing concern of social loneliness in our modern age.
The Rise of Loneliness: A Global Crisis
In 2024, loneliness statistics worldwide show a significant rise in individuals who identify as feeling lonely or socially isolated. Studies indicate that almost one-third of the global population now suffers from some degree of loneliness. The issue affects both developed and developing countries, transcending age, gender, and social status. But what does this mean, and why is it happening on such a large scale?
According to loneliness epidemic statistics worldwide, loneliness is not merely the absence of social interaction but also a lack of meaningful, satisfying relationships. Social loneliness, which refers to a perceived lack of social connections or relationships, has been on the rise, particularly in urban areas. Rapid urbanization and the fast pace of life in cities can often lead to a sense of disconnection, leaving many to feel isolated amidst the crowds.
Loneliness Across Continents: A Breakdown by Country
Hiheai.com
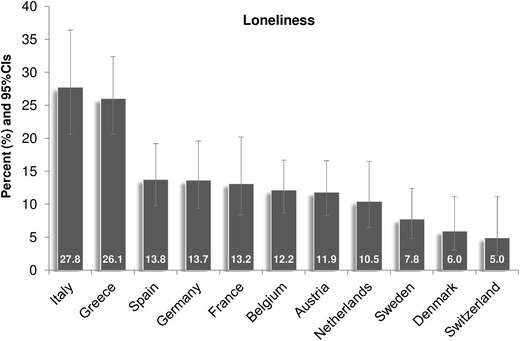
One of the most striking findings in the loneliness epidemic statistics by country is the variation in how loneliness is experienced across different nations and continents. Let’s take a closer look at the trends in some key regions:
-
North America:
In the U.S. alone, a staggering 60% of adults reported feeling lonely on a regular basis. This is a notable rise from previous years, and experts attribute it to increasing societal pressures, the decline of community-based organizations, and the prioritization of work over social life. Canada, too, has seen a similar increase, with nearly half of the population admitting to feeling socially disconnected.
-
Europe:
Many European countries are witnessing a loneliness epidemic, particularly among the elderly. Nations like the UK, Germany, and France have reported a significant percentage of their populations experiencing loneliness, especially after the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2024, it was revealed that over 20% of the population in the UK feels chronically lonely, highlighting the need for social interventions.
-
Asia:
Despite the strong sense of family and community in many Asian cultures, loneliness is becoming a growing issue, especially in urbanized and developed countries like Japan, South Korea, and China. Japan, for example, has long faced the phenomenon of hikikomori, where individuals withdraw from social life. Loneliness among the elderly is also a growing concern in China, with social loneliness epidemic statistics showing that nearly one-fifth of the elderly population experiences significant isolation.
-
Australia and Oceania:
Australia has seen an increase in loneliness, particularly among young people. A 2024 report reveals that 35% of Australians aged 18-24 experience high levels of loneliness, with factors such as social media use, work pressures, and the high cost of living contributing to the issue.
-
Africa and the Middle East:
Although less data is available, social isolation loneliness epidemic statistics indicate that loneliness in Africa and the Middle East is linked to societal and economic factors. Migration for work, poverty, and the break-up of traditional communities contribute to the feeling of loneliness and social disconnection.
Contributing Factors to the Loneliness Epidemic
The reasons behind the loneliness epidemic are multi-faceted. One significant contributor is the rise of technology and social media. While social media platforms can connect people across vast distances, they often fail to provide the depth and quality of in-person interactions. As a result, many people may have numerous digital connections but still feel socially lonely.
The changing dynamics of family structures also play a role. In many countries, there has been a decline in traditional multi-generational households, leaving more people living alone. In urban centers, where the cost of living is high, young professionals are increasingly living solo, which can lead to social isolation.
Moreover, workplace culture in many parts of the world emphasizes productivity and individual achievement over social well-being, resulting in a lack of work-life balance and time for nurturing meaningful relationships.
The Health Impacts of Loneliness
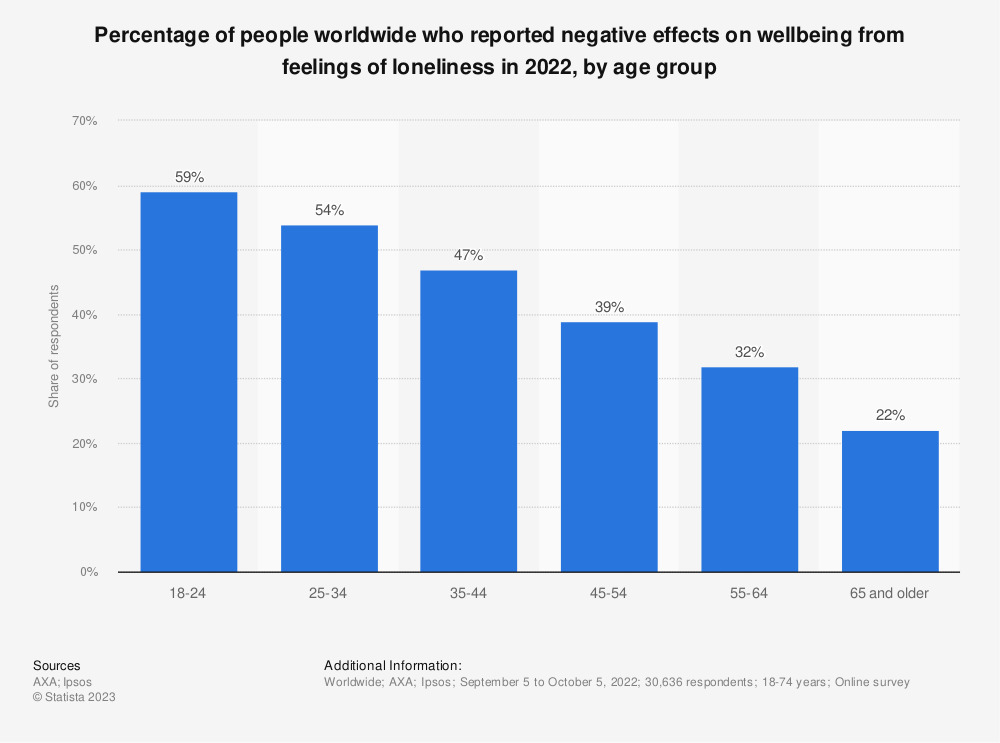
Loneliness is not just a mental or emotional issue; it has significant health implications as well. According to loneliness epidemic statistics, prolonged social isolation and loneliness can lead to a range of health problems, including depression, anxiety, heart disease, and a weakened immune system. In fact, some studies suggest that chronic loneliness can be as harmful as smoking 15 cigarettes a day.
Social loneliness epidemic statistics also show that lonely individuals have a higher likelihood of experiencing cognitive decline as they age. This is particularly concerning given the aging populations in many countries.
Hiheai.com
Steps Toward Combating the Loneliness Epidemic
The global rise in loneliness calls for action at both societal and individual levels. Governments and communities are beginning to recognize loneliness as a public health issue and are implementing measures to address it. For example, the UK has appointed a Minister for Loneliness, and countries like Japan have introduced community centers to encourage social engagement among their aging populations.
At an individual level, it’s crucial to prioritize meaningful relationships over digital interactions. Engaging in local community activities, reaching out to neighbors, and finding common interests through clubs and groups can help combat the feelings of social loneliness.
Conclusion: A Call for Connection
In conclusion, the loneliness epidemic is a worldwide issue affecting millions of people across continents. While technology has connected the world in unprecedented ways, it has also, paradoxically, contributed to feelings of disconnection and isolation. Understanding the global loneliness epidemic statistics is just the first step in addressing this pressing issue. As we move forward in 2024, let’s make an effort to connect more meaningfully, be it through community involvement, face-to-face interactions, or simply by being present for those around us. The key to overcoming the loneliness epidemic lies in fostering genuine, human connections that enrich our lives.



